- 1. The distinct functions of firewalls and SD-WAN
- 2. How firewalls and SD-WAN evolved to overlap
- 3. How does a firewall actually work within SD-WAN?
- 4. Where does inspection occur in the SD-WAN data path?
- 5. What are the main deployment models for firewalling in SD-WAN?
- 6. How centralized management ties firewall and SD-WAN policies together
- 7. When is a standalone firewall still needed?
- 8. How SD-WAN and firewall convergence lays the groundwork for SASE
- 9. SD-WAN firewall FAQs
- The distinct functions of firewalls and SD-WAN
- How firewalls and SD-WAN evolved to overlap
- How does a firewall actually work within SD-WAN?
- Where does inspection occur in the SD-WAN data path?
- What are the main deployment models for firewalling in SD-WAN?
- How centralized management ties firewall and SD-WAN policies together
- When is a standalone firewall still needed?
- How SD-WAN and firewall convergence lays the groundwork for SASE
- SD-WAN firewall FAQs
What Is the Role of a Firewall in SD-WAN Architecture?
- The distinct functions of firewalls and SD-WAN
- How firewalls and SD-WAN evolved to overlap
- How does a firewall actually work within SD-WAN?
- Where does inspection occur in the SD-WAN data path?
- What are the main deployment models for firewalling in SD-WAN?
- How centralized management ties firewall and SD-WAN policies together
- When is a standalone firewall still needed?
- How SD-WAN and firewall convergence lays the groundwork for SASE
- SD-WAN firewall FAQs
The role of a firewall in SD-WAN architecture is to inspect and control network traffic that passes through the SD-WAN fabric according to defined security policies.
It identifies applications, users, and content to enforce segmentation and prevent unauthorized access.
By integrating these functions into the SD-WAN data plane, the firewall ensures secure, consistent traffic handling across branches, data centers, and cloud connections.
The distinct functions of firewalls and SD-WAN
SD-WAN and firewalls both manage traffic. They just do it in different ways.
SD-WAN uses software to decide how data moves across the network.
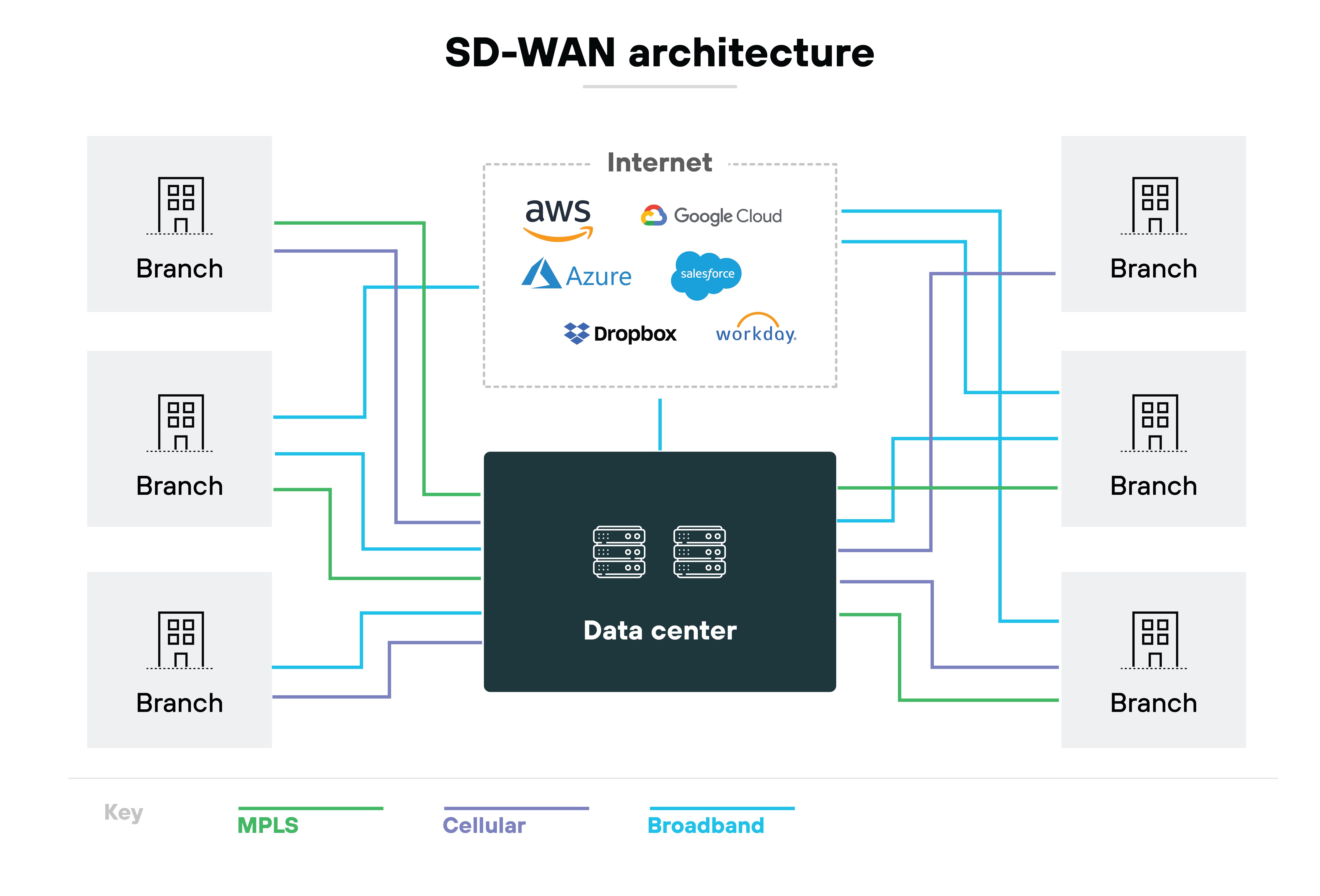
It builds virtual overlays that sit on top of physical connections—like MPLS, broadband, or LTE—and steers traffic based on application type, performance, or policy. In other words, it controls where data goes and how it gets there.
The goal is simple: maintain speed, reliability, and efficiency across every branch and cloud path.
A firewall focuses on what moves through those paths.
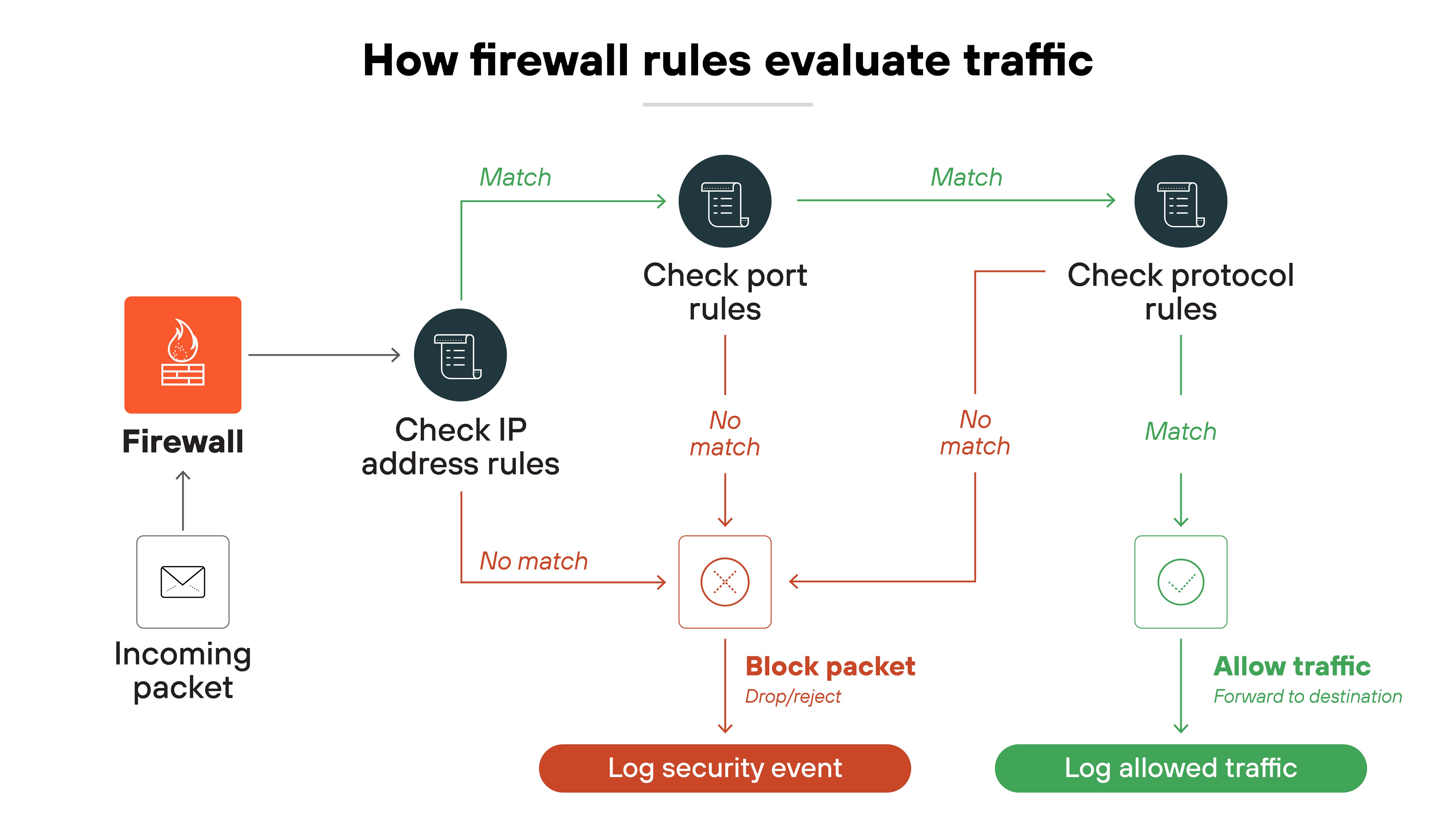
It inspects packets at multiple layers, from basic network information to the application itself. It checks identities, matches sessions to policies, and blocks anything that violates rules or appears unsafe. That includes enforcing segmentation so users and systems only access what they should.
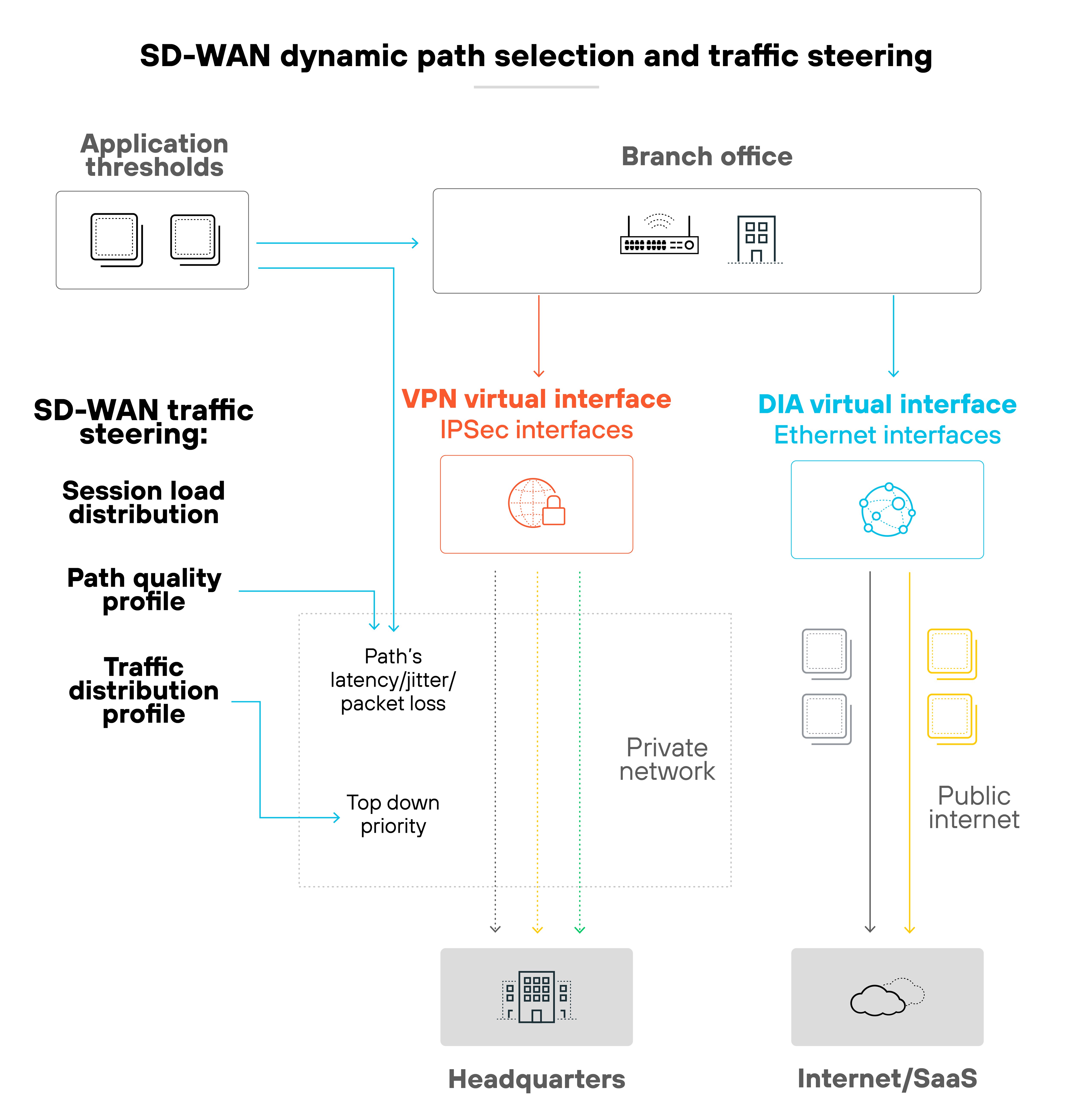
When these functions meet inside one architecture, SD-WAN provides intelligent routing while the firewall enforces security within each path. Together, they create a network that's both optimized and protected—where traffic decisions and security policies operate in sync rather than in isolation.
How firewalls and SD-WAN evolved to overlap
Not long ago, routing and security lived on different planes.
A router decided how to reach a destination. A firewall decided whether that destination was allowed. Both were critical. But both operated in isolation.
In the traditional WAN era, this made sense.
Traffic flowed through centralized data centers. Firewalls sat at the perimeter inspecting every packet that entered or left the network. This model worked when applications and users stayed on-premises. But it couldn't keep up with distributed users, cloud services, and direct internet access.
That shift drove the first stage of convergence.
As organizations adopted SD-WAN, edge devices began handling not just routing but also basic security. Early SD-WAN appliances added simple next-generation firewall capabilities—like stateful inspection and URL filtering—to reduce the need for separate branch firewalls. The goal was to secure new direct-to-internet connections without backhauling traffic to the data center.
Modern architectures take that further.
Today's platforms merge routing and security into one system. The SD-WAN control plane manages path selection and policy distribution, while the data plane runs embedded firewalls that inspect sessions in real time. These firewalls perform deep inspection, segmentation, and threat prevention using on-box or containerized engines.
And now, the boundary is disappearing altogether.
Unified SD-WAN platforms use single-pass inspection and shared management to deliver both networking and security functions seamlessly. At the same time, cloud-delivered services extend those same capabilities through secure access service edge (SASE) and firewall-as-a-service (FWaaS) models.
Ultimately, what began as separate tools has become a unified framework. One that connects users efficiently while enforcing security everywhere they connect.
How does a firewall actually work within SD-WAN?
Firewalls are not just attached to SD-WAN anymore. They're built into it.
To understand how that works, it helps to look at the two planes that define SD-WAN architecture: the control plane and the data plane.
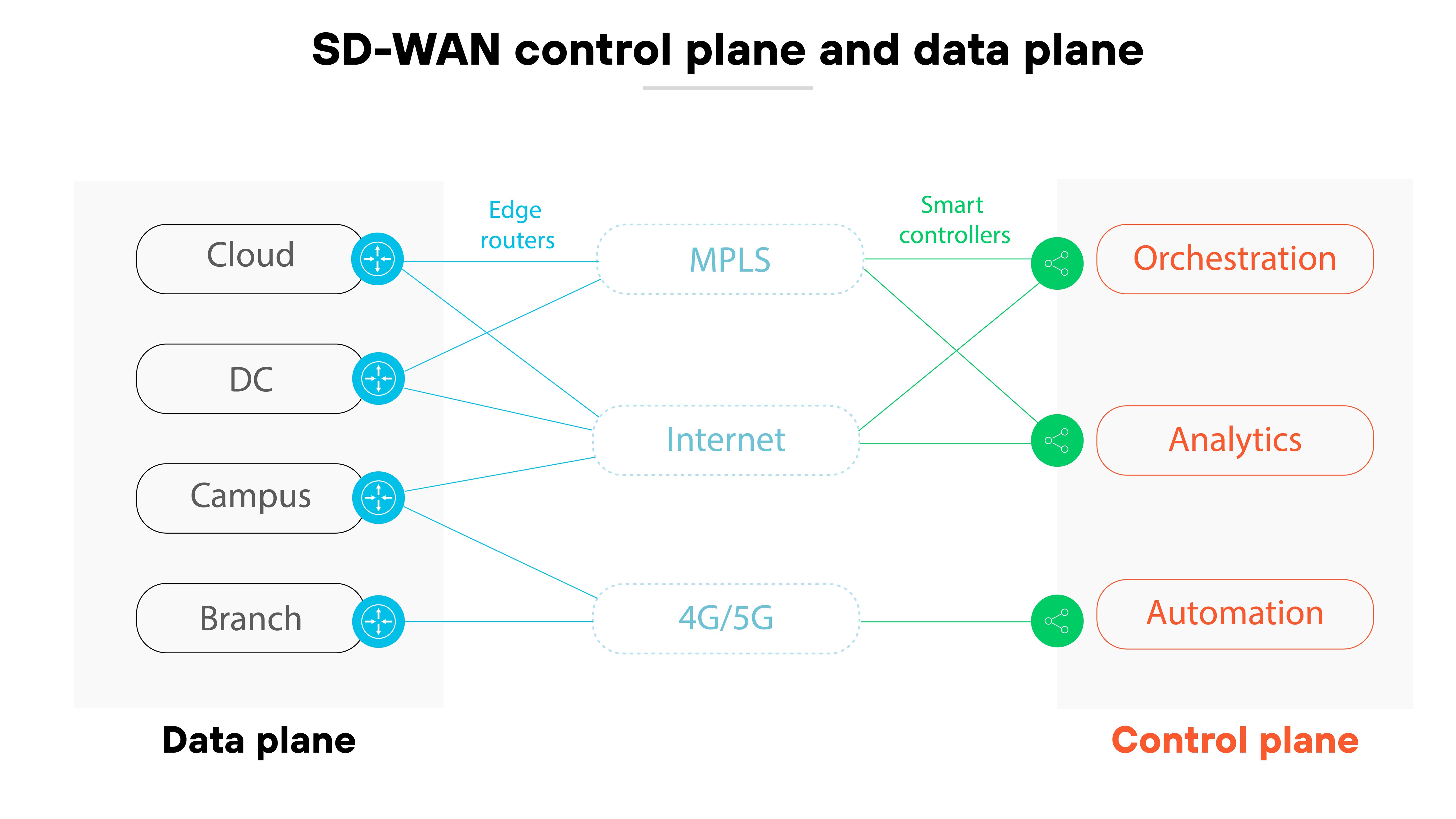
The control plane is where routing and policy decisions are made. It tells the network how to steer traffic, manage tunnels, and apply rules. The data plane is where packets actually move. It carries traffic through encrypted tunnels, applies quality of service, and enforces security policies.
Within the data plane, the firewall is responsible for inspecting and controlling each session:
-
When traffic enters an SD-WAN edge device, it's decrypted if it arrives through an IPSec or SSL tunnel.
The system identifies the application, user, and session context. It then applies next-generation firewall policies, checking for compliance with access rules, intrusion signatures, and threat indicators.
-
If the session is permitted, the data is classified, filtered, and re-encrypted for its next hop.
This ensures that inspection happens before the packet reenters the overlay network. In other words, security is enforced locally at the branch instead of being backhauled through a central gateway.
-
Segmentation adds another layer of control.
Traffic is grouped into logical zones or virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instances, so each business function or user group stays isolated. The firewall enforces policies within and between these segments, preventing lateral movement and maintaining compliance boundaries.
It's worth noting that inspection placement does depend on network design.
Some organizations perform it locally on each edge device for immediate enforcement. Others centralize inspection at regional hubs. And cloud-based models extend those same controls to remote users through firewall-as-a-service or SASE platforms.
The result is consistent policy enforcement across every connection—branch, data center, or cloud—without disrupting how SD-WAN optimizes traffic flow.
Where does inspection occur in the SD-WAN data path?
Inspection happens everywhere traffic crosses a boundary.
But understanding where that inspection takes place—and in what order—makes all the difference in how secure and efficient the network really is.
In most SD-WAN architectures, traffic is inspected before encryption.
When packets enter the SD-WAN edge, they're decrypted if necessary, then inspected by the firewall before being re-encapsulated into the overlay tunnel. This allows the firewall to view full packet contents, apply policies, and block threats before data is hidden by encryption.
If inspection happened only after encryption, the system couldn't analyze payloads or enforce application-level controls.
Here's why order matters.
Encrypted traffic that skips local inspection must be sent elsewhere—often to a central hub or cloud security service—for decryption and analysis. And that introduces latency. Which means decentralized inspection, closer to the user or branch, generally delivers faster performance while maintaining protection.
Topology plays a role too.
In hub-and-spoke designs, inspection often happens at the hub, where all branch traffic converges. In full mesh topologies, each branch can inspect and secure its own traffic locally. Hybrid models combine both, inspecting sensitive traffic at the hub while allowing direct, secure connections between trusted sites.
Cloud-delivered models take this one step further.
Firewall-as-a-service and SASE platforms extend inspection into the cloud itself. In this model, encrypted traffic is sent to the nearest service edge, decrypted, inspected, and re-encrypted before continuing to its destination. It unifies local and remote inspection under consistent policy enforcement.
The takeaway:
Inspection placement defines how quickly and thoroughly threats are detected. Placing it before encryption—and as close to the user as possible—keeps SD-WAN secure without sacrificing performance.
What are the main deployment models for firewalling in SD-WAN?
Firewalls can be deployed in several ways within an SD-WAN. Each approach defines where traffic is inspected and how policies are enforced.
In practice, most networks use a combination of three models: local, centralized, and cloud enforcement. Each has a clear role and distinct trade-offs.
Let's take a closer look at each:
Local enforcement
Local enforcement means the firewall runs directly on the SD-WAN edge device. It could be a built-in function, a virtualized container, or an NGFW.
When traffic enters or leaves a branch, it's decrypted, inspected, and re-encrypted right there on-site. This keeps decisions close to the user, minimizing latency and maintaining session context.
It's ideal for sites that need real-time performance or handle sensitive applications locally.
The trade-off is potential operational complexity.
Distributed inspection requires consistent policy management across multiple devices. That's why centralized orchestration is key. So every branch enforces the same standards without manual upkeep.
Centralized enforcement
In centralized models, inspection happens at a data center or regional hub. All branch traffic flows through these aggregation points for decryption, inspection, and policy control.
This setup simplifies operations. Security teams can manage fewer inspection points and maintain tighter policy oversight. It also works well for traffic that must pass through core systems or comply with regulatory inspection requirements.
However, backhauling traffic adds latency and increases dependency on hub availability. It's effective for some workloads but less efficient for high-volume, latency-sensitive traffic such as SaaS or video.
Cloud enforcement
Cloud-based enforcement moves inspection into a distributed security service. Traffic is routed to the nearest service edge, where FWaaS or SASE applies the same inspection as an on-prem firewall.
This model scales easily.
It extends consistent policy enforcement to remote users, unmanaged devices, and branch sites without deploying hardware. And it's especially useful for organizations shifting to direct internet access and cloud-hosted applications.
The main consideration is dependency on provider proximity and bandwidth. Performance varies based on where the nearest inspection point resides.
In short:
- Local enforcement favors performance.
- Centralized enforcement favors control.
- Cloud enforcement favors scalability.
Choosing the right mix ensures SD-WAN remains secure, consistent, and efficient wherever traffic originates.
How centralized management ties firewall and SD-WAN policies together
Modern SD-WAN depends on centralized management. It's what allows routing and security to operate as one system instead of two separate layers.
In practice, centralized management platforms form the shared control plane for the entire network. They distribute routing rules, enforce firewall policies, and provide unified visibility into traffic flows.
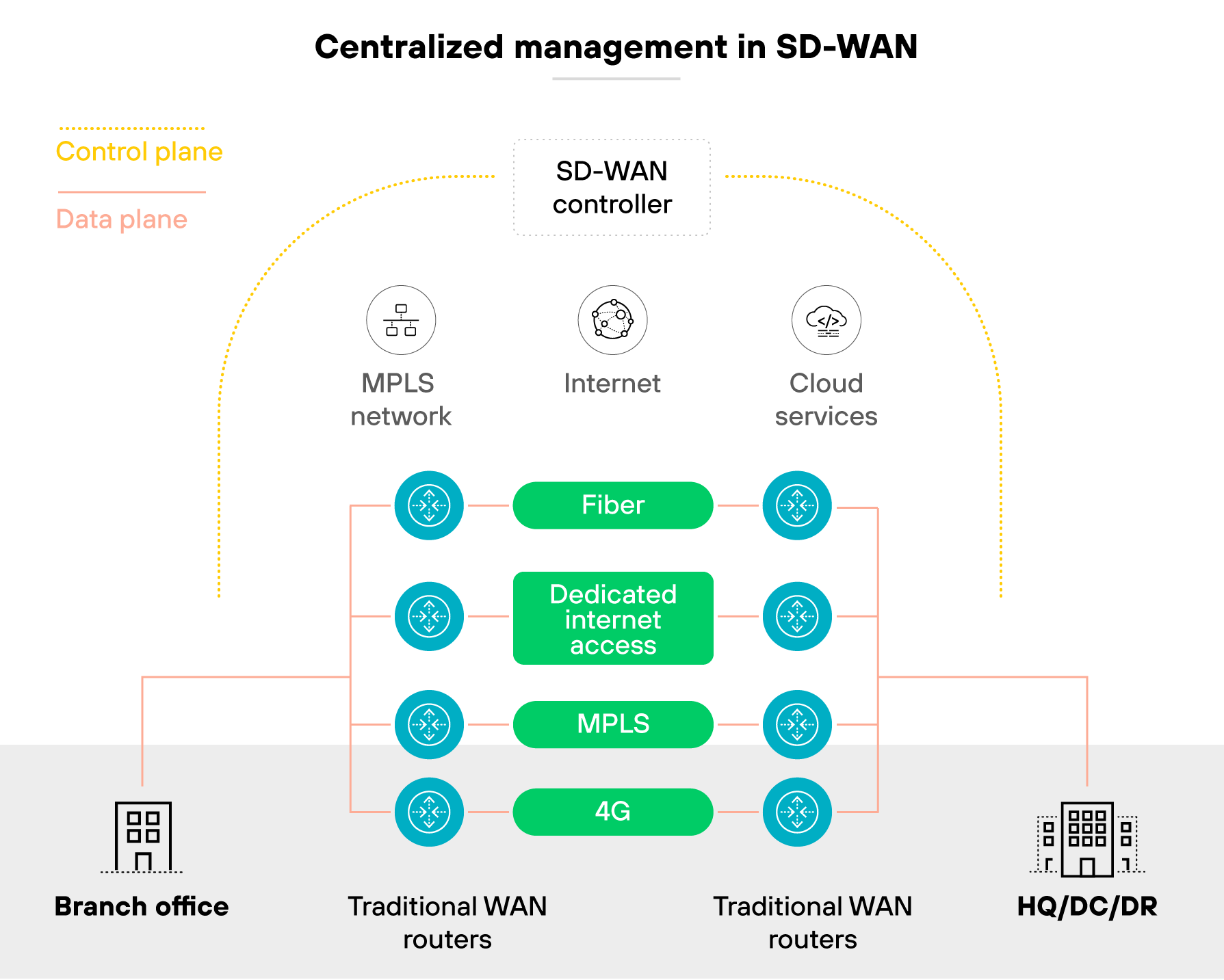
Administrators use these platforms to define intent—like how applications should route, or what types of traffic should be inspected—and then push those configurations across all devices at once.
This is where routing and security truly converge.
Instead of managing them through different interfaces, both functions live in the same policy framework. Routing policies decide the best path based on performance metrics, while firewall policies determine whether that traffic is allowed or blocked.
Because they're coordinated through the same control plane, the SD-WAN can steer and secure traffic in a single, consistent process.
The benefits are significant:
- Policy consistency reduces the risk of misconfiguration, one of the most common causes of network vulnerabilities.
- It also simplifies compliance since all enforcement points follow identical security baselines.
- And when routing and firewall policies are visible in one dashboard, operations teams can diagnose performance and security events together instead of switching between tools.
- Centralized management also makes scale practical. A new branch or user can inherit existing policies immediately without manual configuration. Updates roll out network-wide with version control and audit tracking, keeping governance intact.
- Automation extends this even further, applying policies dynamically as network conditions change.
Essentially centralized management turns SD-WAN from a set of distributed nodes into a unified system of control. It ensures that routing, security, and visibility evolve together, reducing risk while maintaining performance and agility.
When is a standalone firewall still needed?
Even as SD-WAN integrates advanced security, standalone firewalls still play a critical role. They provide capabilities that extend beyond what's practical, or efficient, to embed directly into the SD-WAN edge.
For example, high-throughput data centers rely on dedicated firewalls to handle massive session volumes and specialized traffic inspection. These environments often need more granular control and hardware acceleration than a distributed SD-WAN appliance can deliver.
The same applies to large-scale cloud interconnects or carrier-grade deployments where throughput and resiliency take precedence over edge simplicity.
In regulated industries, segmentation requirements can also drive the need for separate firewalls. Financial, healthcare, and government networks often maintain physically distinct security zones to meet compliance frameworks such as PCI DSS or HIPAA. In those cases, an independent firewall remains the authoritative enforcement point between zones or enclaves.
Standalone firewalls are also necessary for assets that fall outside SD-WAN coverage. That includes legacy infrastructure, industrial systems, or third-party services that connect through different transport methods. These environments depend on traditional perimeter or virtualized firewalls to maintain visibility and policy control.
The key is integration, not replacement.
Secure SD-WAN connects seamlessly with perimeter and cloud-based firewalls, extending policy and telemetry across both. This layered approach preserves centralized management while maintaining the depth of protection large enterprises still require.
Here's the takeaway:
Standalone firewalls remain vital where scale, regulation, or architectural isolation demand them. They complement SD-WAN rather than compete with it, ensuring every layer of the network is secured at the right place and scale.
How SD-WAN and firewall convergence lays the groundwork for SASE
The convergence of SD-WAN and firewalling is what makes SASE and zero trust possible in practice. By combining distributed networking with built-in security enforcement, the network itself becomes the delivery mechanism for consistent, identity-based control.
Here's how it fits together.
SD-WAN provides the distributed data plane that connects users and locations. Integrated firewalls bring inspection and segmentation directly to those connection points.
When policies follow the user instead of the network segment—and access is continuously verified—the result aligns with the core principles of zero trust architecture.
That model is now being extended through SASE. Centralized policy orchestration pushes identity, application, and threat prevention rules to every edge, whether physical or cloud-delivered.
Traffic is steered and inspected based on who the user is, what device they're on, and what they're trying to access. Not just where they connect.
So: SD-WAN creates the path. The firewall enforces trust.
And together, they form the foundation of a network that's adaptive, policy-driven, and ready for SASE's full vision of cloud-based security.
