Cloud Compliance: Protecting Your Data and Maintaining Trust
Over the last decade, we’ve seen a significant shift in the industry toward cloud computing, as many businesses opt to use cloud-native services. This shift has allowed organizations to take advantage of infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) — all of which deliver increased scalability, cost-effectiveness, flexibility and improved efficiency.
While customers use various cloud service providers, their primary concern remains data security. In the current landscape, failure is unacceptable, and noncompliance with regulations leads to stiff penalties. Most critically, noncompliance erodes customer trust, which businesses can’t afford to lose.
Cloud Compliance Defined
Cloud compliance refers to the process of ensuring that an organization's use of cloud-based services, resources and technologies adheres to relevant laws and regulations governing data privacy, security and management. Achieving cloud compliance helps organizations mitigate risks and protect sensitive information.
For example, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which is used to ensure security for payments made with debit or credit cards, has requirements for cloud deployments. The same goes for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the healthcare industry.
Ensuring Security in a Shared Responsibility Model
Security breach headlines continue to roll out, reminding us of the importance of cloud compliance. Consider the Sina Weibo breach, for example. After hackers infiltrated the social media platform, they sold the personal data of approximately 538 million users — names, site usernames, gender, location, phone numbers — on the dark web. U.S. voters took a hit with the S3 bucket breach that resulted in the exposure of personal data of nearly 198 million Americans. And just last month, T-Mobile suffered its second data breach of 2023 after a data leak revealed the PINs, full names and phone numbers of over 800 customers. Incidents like these often result from poorly implemented cloud compliance policies.
It's imperative to realize that, while the foundational data infrastructure provided by the cloud service provider is secure, the customer assumes responsibility for data security and compliance assurance.
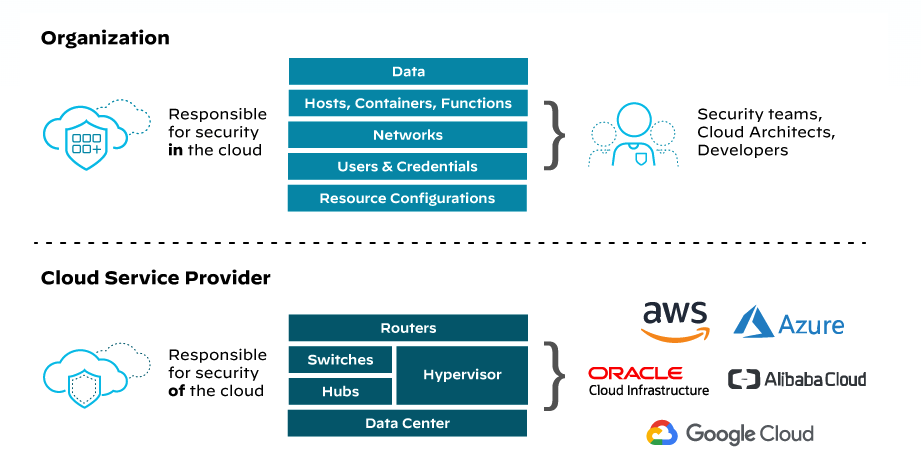
Cloud service providers follow a shared responsibility model, where they take care of the security of the cloud infrastructure, including the physical data centers, network and hardware. But customers retain responsibility for securing their data and configuring compliance controls within the cloud services they use, such as S3 buckets, virtual machines or databases.
For example, when creating an S3 bucket on AWS, the default settings may not be compliant with specific regulations or security requirements. It’s the customer's responsibility to configure the appropriate access controls, encryption, logging and other security measures to ensure the S3 bucket meets their compliance needs.
Key Factors of Cloud Compliance
Implementing an effective cloud compliance policy is crucial for organizations to ensure the security and regulatory adherence of their cloud environments. Let's explore some of these key factors:
- Compliance Governance: Organizations should establish clear compliance objectives aligned with industry regulations and their specific business requirements. This includes understanding the data protection and privacy regulations that apply to their industry and ensuring compliance with those regulations.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment helps identify potential security risks and compliance gaps. Organizations should evaluate potential threats, vulnerabilities and associated risks to their cloud environment. This assessment helps in prioritizing security controls and taking necessary steps to mitigate identified risks.
- Policies and Procedures: Developing well-defined and documented policies and procedures is essential. These policies should cover areas such as access controls, encryption, data handling, incident response and data breach notification. Regularly review and update these policies to ensure they reflect the current regulatory landscape and emerging threats.
- Monitoring and Auditing: The continuous monitoring of the cloud environment helps identify and rectify any noncompliance issues or security incidents promptly. Implementing robust monitoring solutions can detect anomalies, unauthorized access attempts, or policy violations. Regular audits assess the effectiveness of security controls and pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Incident Response and Remediation: Develop an incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a security incident or data breach. Ensure the plan includes procedures for containment, investigation, notification and recovery. Regularly test and update the plan to address emerging threats and lessons learned from previous incidents.
The Role of Prisma Cloud in Cloud Compliance
Prisma Cloud provides the industry's broadest security compliance coverage for infrastructure, workloads and applications throughout the development lifecycle and across hybrid and multicloud environments.
Helping executive teams and security engineers effectively manage and maintain compliance, Prisma Cloud provides the following capabilities:
Continuous Monitoring
Prisma Cloud continuously monitors cloud resources and assesses their compliance status in real time. It automatically detects changes that impact compliance and can alert security teams to take corrective actions.
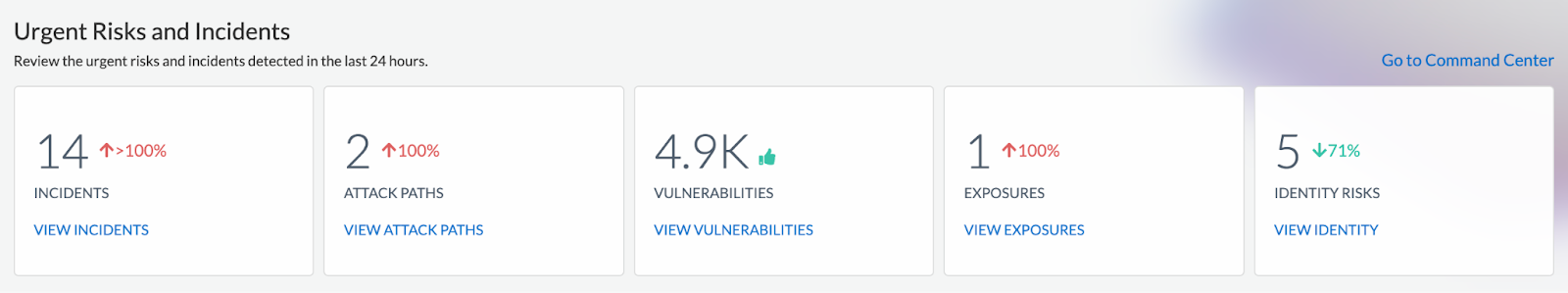
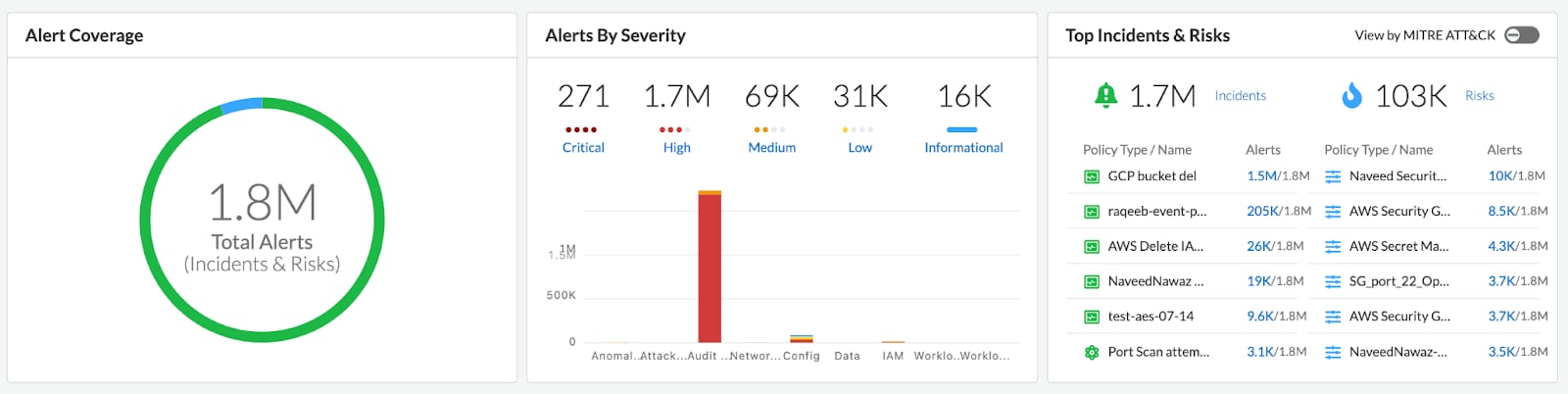
Granular Visibility
Prisma Cloud offers granular visibility into cloud resources, providing detailed information about individual assets and their compliance status. This allows security teams to drill down into specific assets to understand the exact reasons behind noncompliance.
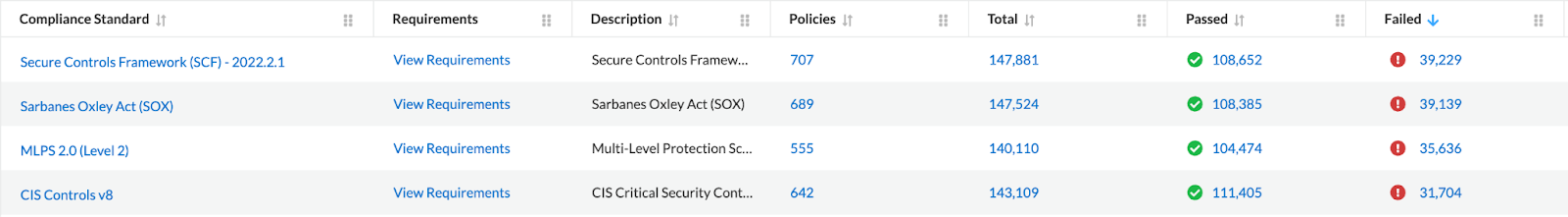
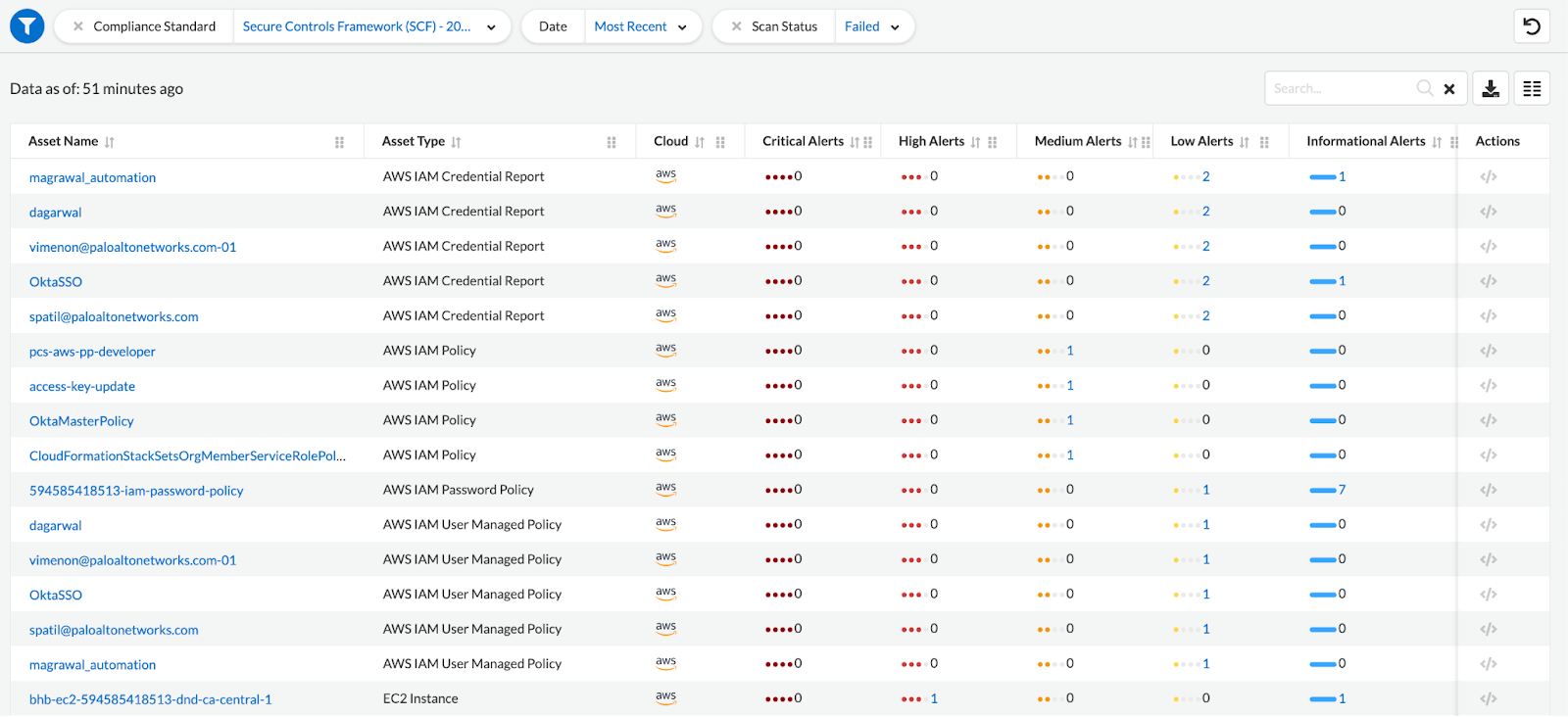
Compliance Reporting
Prisma Cloud generates compliance reports that provide a comprehensive view of the compliance status of assets in the cloud environment. These reports highlight noncompliant resources, misconfigurations and policy violations, enabling organizations to identify and address compliance gaps.
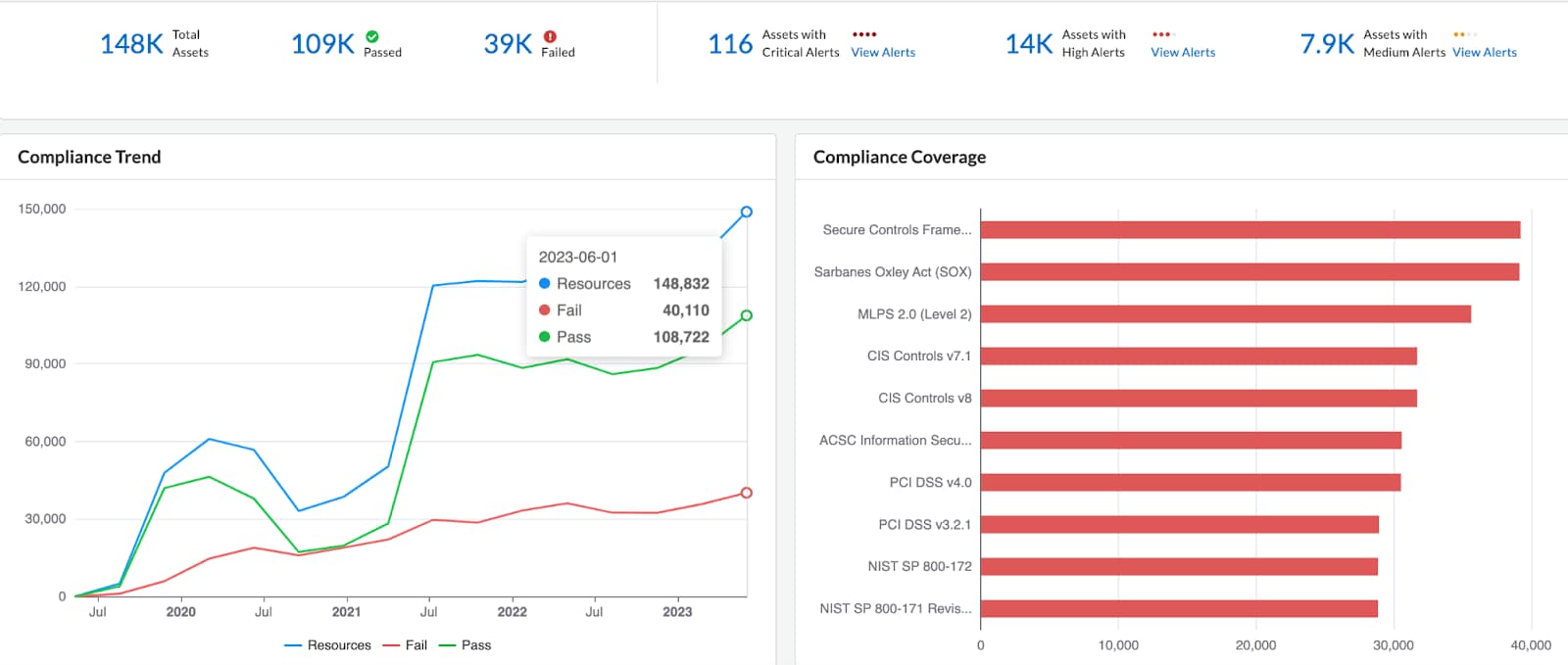
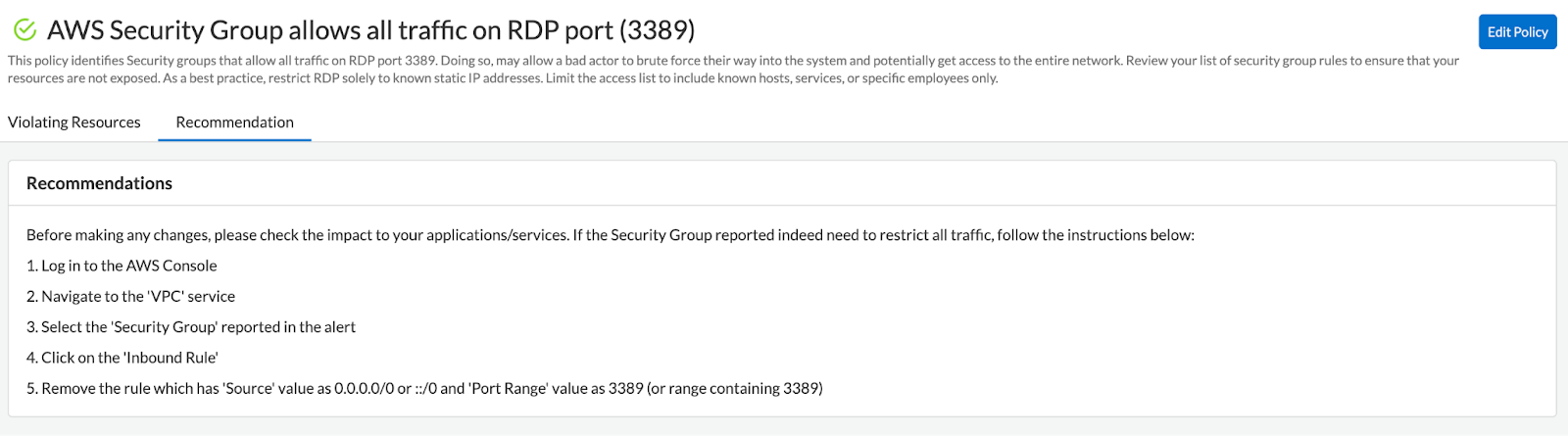
Remediation Recommendations
Prisma Cloud provides actionable recommendations and remediation steps to address compliance issues. It suggests specific configuration changes or security controls that organizations should implement to bring assets into compliance with industry regulations and organizational policies.
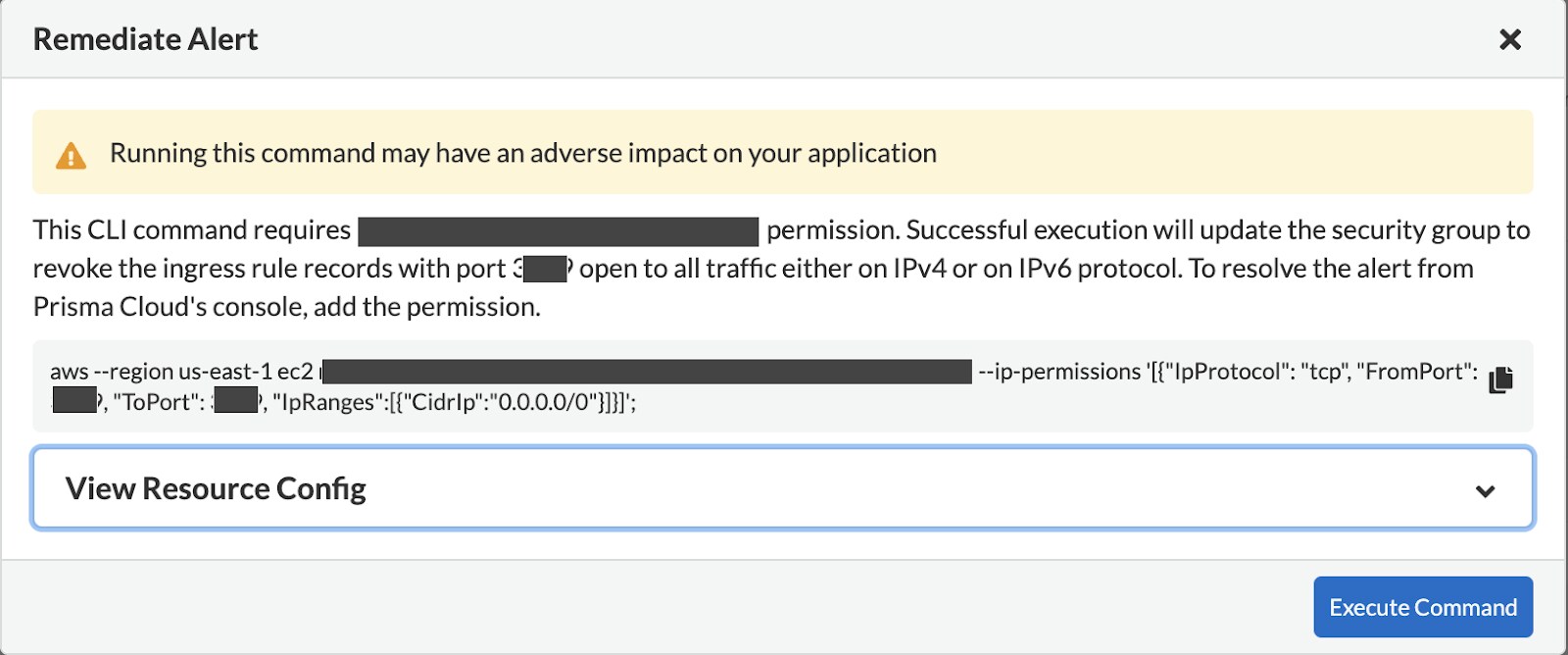
Prisma Cloud helps customers to achieve and maintain compliance within their cloud environments. Significant regulations supported by Prisma Cloud include:
- CIS Controls: Prioritized safeguards known as CIS controls help to counter the most common cyberattacks against systems and networks. Derived from the consensus list of security controls, experts in security consider CIS Controls the top defensive techniques to prevent data breaches and lessen the damage caused by cyberattacks.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The Framework outlines various methods for data protection, contributing to a more secure organization. It employs a consistent procedure to ensure assets are adequately shielded from malicious actors and code. Ideally, the Framework comprises five steps: identify, protect, detect, respond, recover.
- ISO/IEC 27001: Recognized globally as the standard for information security management systems (ISMS), ISO/IEC 27001 is essential. Any company handling sensitive data should seriously think about incorporating ISO 27001 into their compliance portfolio.
- Hitrust CSF: The healthcare sector generally drives and controls HITRUST enforcement, while HIPAA establishes specific consequences for data security violations. The industry, including hospitals and payer requiring certification, has seen swift adoption of HITRUST and it is gaining ground as an expectation for service providers and vendors.
Bottom line: Cloud compliance is a crucial aspect of adopting and using cloud services securely and responsibly. It involves adhering to regulatory requirements, industry standards and best practices to ensure the protection of sensitive data and build trust with customers.
Achieve Compliance from a Single Solution
Get real-time and historical views into your compliance status for hosts, containers and serverless functions with Prisma Cloud. Start your free 30-day test drive today — and learn how customers have used Prisma Cloud to improve the security posture of their organizations.
Related Blogs
Subscribe to Cloud Native Security Blogs!
By submitting this form, you agree to our Terms of Use and acknowledge our Privacy Statement. Please look for a confirmation email from us. If you don't receive it in the next 10 minutes, please check your spam folder.